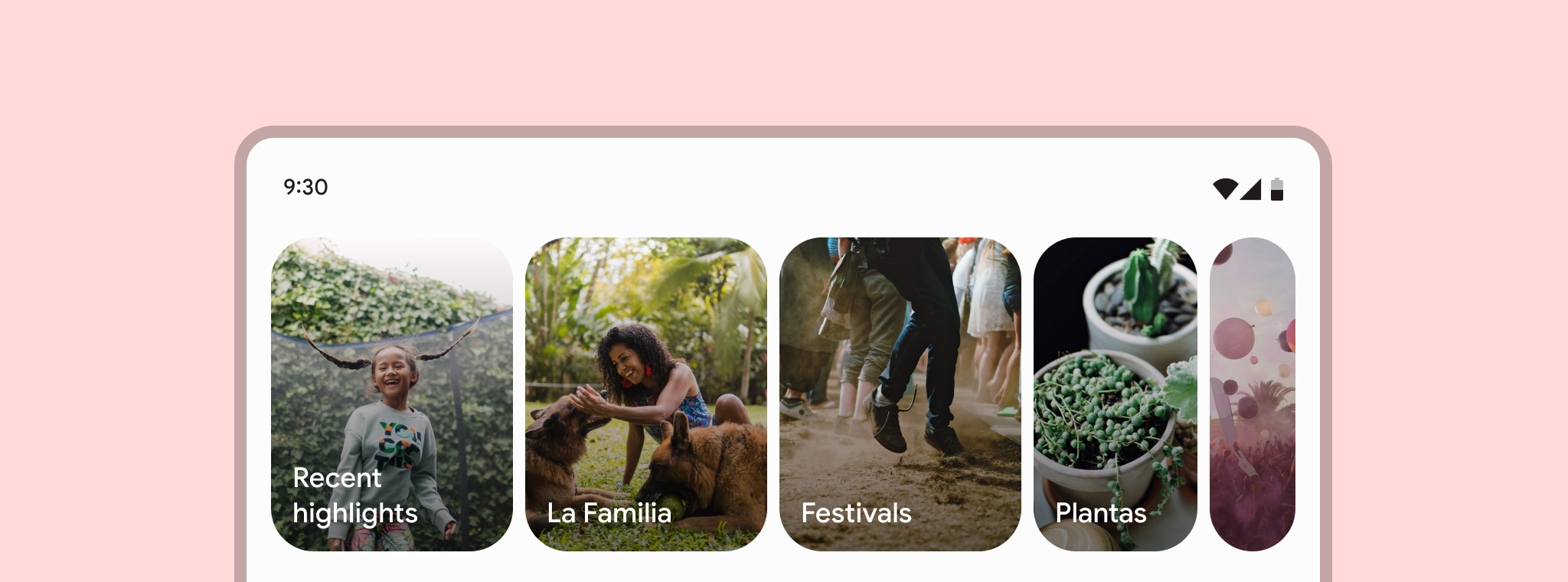
概述
Carousel 直译为圆形传送带,在 Material 3 的设计规范 1 中,主要的特点是
- Carousel 中多个项目 水平滚动
- Carousel 主要是展示视图,并且可以选择包含简短的文本
- Carousel 展示为不同尺寸,滚动时每一项的尺寸动态改变
目前在 Google 官方支持中,MDC-Android 首先支持,本文在于介绍 MDC-Android 中如何结合 RecyclerView 来实现 Carousel 的展示。
基于
MDC-Android 1.9.02 。目前 Carousel 仍处于一个试验性阶段,还有一些设计规范内的细节未被正确实现。
动效展示:
如何使用 Carousel 请参考 MDC-Android 中 Carousel 快速上手,下文中以已经成功使用了 Carousel 为前提来介绍。
何时可使用 Carousel
Carousel 的主要特点是可变的尺寸和内容的视差变化,从官方设计文档的主要示例上来看,主要演示在相册中作为相簿的应用。总结一下,可以认为,如果某个列表入口,信息简要且带有图片信息,可以用 Carousel 来作为展示入口。
虽然它的主体展示内容是图片,但是并不建议使用 Carousel 做纯粹的图片展示,有几个原因
- 图片被
MaskableFrameLayout包裹后,可能被裁切,若要写图片的转场动画时,交互体验不太好(如果只是展示而不需要有点击后的下一步操作也可以忽略这一点);- 目前的 Carousel 控件要求每一个 item 的宽高都是固定的,纯图片的场景不一定能符合要求。
Carousel 中的关键实现
CarouselLayoutManager:用于设置给RecyclerView,计算布局位置MaskableFrameLayout:作为每个item的容器,用于展现动态尺寸改变和视差效果
CarouselLayoutManager
在 MDC-Android 的 Carousel 文档中描述了 item 尺寸的含义。
<译> 改变 Carousel 外观的主要手段是通过设置你的 RecyclerView 的高度和 item 的 MaskableFrameLayout 的宽度。CarouselLayoutManager 将使用 item 布局中设置的宽度,来确定项目在完全展示时应该有的尺寸。这个宽度需要被设置为特定的 dp 值,不能被设置为 wrap_content 。 CarouselLayoutManager 会尝试使用一个尽可能接近你的项目布局的指定宽度的尺寸,但可能会根据 RecyclerView 的可用空间增加或减少这个尺寸。这是在 RecyclerView 的范围内创建一个令人愉快的项目安排所需要的。此外,CarouselLayoutManager` 将只读取和使用第一个列表项上设置的宽度。所有剩下的项目将使用第一个项目的宽度来布置。
简而言之,item 布局中必须声明一个特定的 dp 值,才能进行下一步的操作,尽管这个值并非一定是最终被使用的宽度。
在 CarouselLayoutManager 中,一个十分重要的类是 CarouselStrategy ,它用于计算每一个 item 当前应当是什么宽度。
/**
* A class responsible for creating a model used by a carousel to mask and offset views as they move
* along a scrolling axis.
*/
public abstract class CarouselStrategy {
abstract KeylineState onFirstChildMeasuredWithMargins(
@NonNull Carousel carousel, @NonNull View child);
@FloatRange(from = 0F, to = 1F)
static float getChildMaskPercentage(float maskedSize, float unmaskedSize, float childMargins) {
return 1F - ((maskedSize - childMargins) / (unmaskedSize - childMargins));
}
}
Google 对此抽象类的实现是 MultiBrowseCarouselStrategy 。
其中对计算应绘制到屏幕上的 item 的关键代码为 onFirstChildMeasuredWithMargins
KeylineState onFirstChildMeasuredWithMargins(@NonNull Carousel carousel, @NonNull View child) {
float availableSpace = carousel.getContainerWidth();
LayoutParams childLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
float childHorizontalMargins = childLayoutParams.leftMargin + childLayoutParams.rightMargin;
float smallChildWidthMin = getSmallSizeMin(child.getContext()) + childHorizontalMargins;
float smallChildWidthMax = getSmallSizeMax(child.getContext()) + childHorizontalMargins;
float measuredChildWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
float targetLargeChildWidth = min(measuredChildWidth + childHorizontalMargins, availableSpace);
// Ideally we would like to create a balanced arrangement where a small item is 1/3 the size of
// the large item and medium items are sized between large and small items. Clamp the small
// target size within our min-max range and as close to 1/3 of the target large item size as
// possible.
float targetSmallChildWidth =
MathUtils.clamp(
measuredChildWidth / 3F + childHorizontalMargins,
getSmallSizeMin(child.getContext()) + childHorizontalMargins,
getSmallSizeMax(child.getContext()) + childHorizontalMargins);
float targetMediumChildWidth = (targetLargeChildWidth + targetSmallChildWidth) / 2F;
// Create arrays representing the possible count of small, medium, and large items. These are
// not in an asc./dec. order but are in order of priority. A small count array of { 2, 3, 1 }
// says that ideally an arrangement with 2 small items is found, then 3 is next most desirable,
// then finally 1.
int[] smallCounts = SMALL_COUNTS;
int[] mediumCounts = forceCompactArrangement ? MEDIUM_COUNTS_COMPACT : MEDIUM_COUNTS;
// Find the minimum space left for large items after filling the carousel with the most
// permissible medium and small items to determine a plausible minimum large count.
float minAvailableLargeSpace =
availableSpace
- (targetMediumChildWidth * maxValue(mediumCounts))
- (smallChildWidthMax * maxValue(smallCounts));
int largeCountMin = (int) max(1, floor(minAvailableLargeSpace / targetLargeChildWidth));
int largeCountMax = (int) ceil(availableSpace / targetLargeChildWidth);
int[] largeCounts = new int[largeCountMax - largeCountMin + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < largeCounts.length; i++) {
largeCounts[i] = largeCountMax - i;
}
Arrangement arrangement =
findLowestCostArrangement(
availableSpace,
targetSmallChildWidth,
smallChildWidthMin,
smallChildWidthMax,
smallCounts,
targetMediumChildWidth,
mediumCounts,
targetLargeChildWidth,
largeCounts);
float extraSmallChildWidth = getExtraSmallSize(child.getContext()) + childHorizontalMargins;
float start = 0F;
float extraSmallHeadCenterX = start - (extraSmallChildWidth / 2F);
float largeStartCenterX = start + (arrangement.largeSize / 2F);
float largeEndCenterX =
largeStartCenterX + (max(0, arrangement.largeCount - 1) * arrangement.largeSize);
start = largeEndCenterX + arrangement.largeSize / 2F;
float mediumCenterX =
arrangement.mediumCount > 0 ? start + (arrangement.mediumSize / 2F) : largeEndCenterX;
start = arrangement.mediumCount > 0 ? mediumCenterX + (arrangement.mediumSize / 2F) : start;
float smallStartCenterX =
arrangement.smallCount > 0 ? start + (arrangement.smallSize / 2F) : mediumCenterX;
float extraSmallTailCenterX = carousel.getContainerWidth() + (extraSmallChildWidth / 2F);
float extraSmallMask =
getChildMaskPercentage(extraSmallChildWidth, arrangement.largeSize, childHorizontalMargins);
float smallMask =
getChildMaskPercentage(
arrangement.smallSize, arrangement.largeSize, childHorizontalMargins);
float mediumMask =
getChildMaskPercentage(
arrangement.mediumSize, arrangement.largeSize, childHorizontalMargins);
float largeMask = 0F;
KeylineState.Builder builder =
new KeylineState.Builder(arrangement.largeSize)
.addKeyline(extraSmallHeadCenterX, extraSmallMask, extraSmallChildWidth)
.addKeylineRange(
largeStartCenterX, largeMask, arrangement.largeSize, arrangement.largeCount, true);
if (arrangement.mediumCount > 0) {
builder.addKeyline(mediumCenterX, mediumMask, arrangement.mediumSize);
}
if (arrangement.smallCount > 0) {
builder.addKeylineRange(
smallStartCenterX, smallMask, arrangement.smallSize, arrangement.smallCount);
}
builder.addKeyline(extraSmallTailCenterX, extraSmallMask, extraSmallChildWidth);
return builder.build();
}
其中用于估算出尺寸占用的关键变量:
| 变量 | 作用 |
|---|---|
targetLargeChildWidth | 表示当 item 尺寸最大时宽度应为多少,取 item 的固定宽和 RecyclerView 宽度二者的最小值 |
targetSmallChildWidth | 表示当 item 尺寸最小时的宽度应为多少,默认为 item 的固定宽度的三分之一 |
targetMediumChildWidth | 上述两者和的一半 |
这里涉及到一个分配关系,在上述代码中,会计算当前应该显示多少个 item ,先根据容器的宽度计算出可容纳多少 大、中、小 尺寸的 item 。
- 容器
- 大尺寸 item
- 中尺寸 item
- 小尺寸 item
代码中根据一个 int 数组来规划 item 如何分布。
其中,中尺寸和小尺寸的分布规则是固定的静态数组,如下。
private static final int[] SMALL_COUNTS = new int[] {1};
private static final int[] MEDIUM_COUNTS = new int[] {1, 0};
大尺寸的数组则是,先根据以上规则算出可分配给大尺寸 item 的空间是多少,再由剩余空间确定大尺寸可展示的 item 数量。上述数组的含义为
SMALL_COUNTS代表不论如何都要有 1 个小尺寸的 itemMEDIUM_COUNTS代表可以有 1 个中尺寸 item ,也可以没有
float minAvailableLargeSpace =
availableSpace
- (targetMediumChildWidth * maxValue(mediumCounts))
- (smallChildWidthMax * maxValue(smallCounts));
int largeCountMin = (int) max(1, floor(minAvailableLargeSpace / targetLargeChildWidth));
int largeCountMax = (int) ceil(availableSpace / targetLargeChildWidth);
int[] largeCounts = new int[largeCountMax - largeCountMin + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < largeCounts.length; i++) {
largeCounts[i] = largeCountMax - i;
}
可以看到,minAvailableLargeSpace 是容器宽度减去小尺寸 item 总宽,再减去中尺寸 item 宽。由于目前 MultiBrowseCarouselStrategy 中,中小尺寸的分布规则是固定的,所以他们的数量都是 1 。
其中小尺寸 item 较特殊,在实际交互中它的尺寸是从
smallChildWidthMax到smallChildWidthMin变化的,因此计算时使用其最大值来算空间。<dimen name="m3_carousel_small_item_size_min">40dp</dimen> <dimen name="m3_carousel_small_item_size_max">56dp</dimen>
经过上述步骤获取出估算的容器可容纳的布局后,进入 Arrangement.findLowestCostArrangement 根据上述数量,算出可用的、尺寸消耗最小的排列方式。
Arrangement.findLowestCostArrangement
↓
Arrangement()
↓
Arrangement.fit
↓
Arrangement.calculateLargeSize
在 fit 这一步中 item 的尺寸也会被重新分配。
largeSize =
calculateLargeSize(availableSpace, smallCount, smallSize, mediumCount, largeCount);
mediumSize = (largeSize + smallSize) / 2F;
在 calculateLargeSize 函数中,换算出在当前搭配下,大尺寸 item 的宽度应是多少。
private float calculateLargeSize(
float availableSpace, int smallCount, float smallSize, int mediumCount, int largeCount) {
// Zero out small size if there are no small items
smallSize = smallCount > 0 ? smallSize : 0F;
return (availableSpace - (((float) smallCount) + ((float) mediumCount) / 2F) * smallSize)
/ (((float) largeCount) + ((float) mediumCount) / 2F);
}
逐字分析一下, 容器空间 - ((小尺寸数量 + 中尺寸数量 / 2) * 小尺寸宽度) / (大尺寸数量 + 中尺寸数量 / 2) 。
算出来后,如果 largeSize 和 targetLargeSize 对不上,则进行以下处理。
if (mediumCount > 0 && largeSize != targetLargeSize) {
float targetAdjustment = (targetLargeSize - largeSize) * largeCount;
float availableMediumFlex = (mediumSize * MEDIUM_ITEM_FLEX_PERCENTAGE) * mediumCount;
float distribute = min(abs(targetAdjustment), availableMediumFlex);
if (targetAdjustment > 0F) {
// Reduce the size of the medium item and give it back to the large items
mediumSize -= (distribute / mediumCount);
largeSize += (distribute / largeCount);
} else {
// Increase the size of the medium item and take from the large items
mediumSize += (distribute / mediumCount);
largeSize -= (distribute / largeCount);
}
}
和文首提到的一致,item 尺寸会在绘制前计算出最终的值,和布局中设置的固定 dp 值并不会完全相同。
至此,绘制到屏幕上的首个画面所需的尺寸数据就已经充分了。
而在滑动的过程中,会不断的调用 layoutChildren 来触发界面重新布局。此时一个重要的类是 KeylineStateList ,其中保存着每一个 item 的 Keyline 。滑动过程中,layoutChildren 会根据计算得出的 Keyline 来绘制对应的 item 位置和大小。
/**
* A data class that represents a state an item should be in when its center is at a position
* along the scroll axis.
*/
static final class Keyline {
final float loc;
final float locOffset;
final float mask;
final float maskedItemSize;
// ...
}
| 成员 | 作用 |
|---|---|
loc | item 在滚动轴中的位置。 |
locOffset | 当 item 在 carousel 中心时,它在滚动轴中的位置。 |
mask | item 被遮盖的百分比。 |
maskedItemSize | 当 item 被遮盖时的尺寸。 |
这个计算过程的调用栈为
LayoutManager.layoutChildren
↓
CarouselLayoutManager.updateCurrentKeylineStateForScrollOffset
↓
KeylineStateList.getShiftedState
↓
KeylineStateList.lerp
↓
KeylineState.lerp
↓
Keyline.lerp
最后出现的 lerp 是通过 起始值、结束值、动画百分比,来推算出当前值的函数。
MaskableFrameLayout
MaskableFrameLayout 主要是实现了 Maskable 接口。
/** Interface for any view that can clip itself and all children to a percentage of its size. */
interface Maskable {
/**
* Set the percentage by which this {@link View} should mask itself along the x axis.
*
* @param percentage 0 when this view is fully unmasked. 1 when this view is fully masked.
*/
void setMaskXPercentage(@FloatRange(from = 0F, to = 1F) float percentage);
/**
* Gets the percentage by which this {@link View} should mask itself along the x axis.
*
* @return a float between 0 and 1 where 0 is fully unmasked and 1 is fully masked.
*/
@FloatRange(from = 0F, to = 1F)
float getMaskXPercentage();
/** Gets a {@link RectF} that this {@link View} is masking itself by. */
@NonNull
RectF getMaskRectF();
/**
* Sets an {@link OnMaskChangedListener}.
*
* @param listener a listener to receive callbacks for changes in the mask or null to clear the
* listener.
*/
void setOnMaskChangedListener(@Nullable OnMaskChangedListener listener);
}
此处的关键点在于 setMaskXPercentage ,在 CarouselLayoutManager.updateChildMaskForLocation 中就是通过这一函数来更新每个 item 的遮罩范围的。最终触发了 maskableDelegate 来对遮罩进行更新。
private void onMaskChanged() {
if (getWidth() == 0) {
return;
}
// Translate the percentage into an actual pixel value of how much of this view should be
// masked away.
float maskWidth = AnimationUtils.lerp(0f, getWidth() / 2F, 0f, 1f, maskXPercentage);
maskRect.set(maskWidth, 0F, (getWidth() - maskWidth), getHeight());
maskableDelegate.onMaskChanged(this, maskRect);
if (onMaskChangedListener != null) {
onMaskChangedListener.onMaskChanged(maskRect);
}
}
对于 maskableDelegate 我们可以看到主要是对不同 API 层上做的适配。
private MaskableDelegate createMaskableDelegate() {
if (VERSION.SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU) {
return new MaskableDelegateV33(this);
} else if (VERSION.SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP_MR1) {
return new MaskableDelegateV22(this);
} else {
return new MaskableDelegateV14();
}
}